Background
This year, Privacy and Scaling Exploration (PSE) has supported an innovative project: a blockchain-powered eSIM. Three grantees, Arpit, Tanmay, and Manul, are developing this project.
The project has been supported by PSE for the following reasons:
- Introducing cryptography to the telecom industry, particularly in virtual network operations.
- Using cryptography for secure remote provisioning of eSIMs.
- Enhancing privacy with zero-knowledge proofs.
- Scaling Ethereum for widespread adoption using account abstraction and other smart contract methods.
- Allowing day-to-day users to experience owning a crypto wallet without overwhelming information.
Blockchain-powered eSIM, Technology detail
The tech stack includes Smart Contract and Ethereum, Passkeys and Account Abstraction, Proxy Backend Server and react Native.
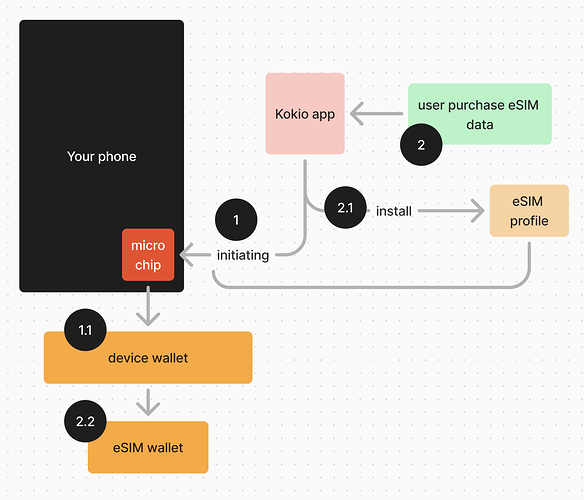
- Smart Contracts and Ethereum is responsible for issuing smart wallets for eSIMs. The eSIM Wallet smart contract suite consists of a group of smart contracts which work together to deploy, record and maintain eSIM related data and functionalities. Using the smart contracts, the user can pay for their data bundle subscriptions. There are multiple smart contracts that make this possible:
-
Registry Contract - Responsible for deploying both the factory contracts (Device Wallet Factory and ESIM Wallet Factory). It also acts as a registry for keeping note of all the Device Wallets and ESIM Wallets deployed and marks them as valid. Any Device Wallet or ESIM Wallet deployed outside the contract suite might be unknown to the Registry and will be considered invalid. Users can interact with the Registry contract to deploy their first Device and ESIM wallet.
-
Device Wallet Factory - Responsible for deploying device wallet smart contracts and maintaining device wallet related data.
-
Device Wallet Smart Contract - Every user (ETH address of the master keystore created by the eSIM wallet app) has a unique device wallet per mobile device.
Users can use the device wallet as their personal smart contract wallet to store ETH and other ERC-20 tokens and have full ownership of the wallet.
-
eSIM Wallet Factory - Responsible for deploying all the eSIM wallet smart contracts. Only the eSIM smart contracts deployed by this factory will be valid smart contracts.
-
eSIM Wallet Smart Contract - Each eSIM is associated with a unique eSIM wallet smart contract. This eSIM wallet is an on-chain representation of the eSIM and allows user to buy the data bundles.
-
- Passkeys and Account Abstraction is responsible for smart wallet that allows users to do more in crypto space other from purchasing eSIM. Users can use it as normal ERC-20 smart wallet.
- Proxy Backend Server is to interact with eSIM Provider APIs for managing eSIM, storing sensitive information in a centralised database and others information on-chain.
Broadly, the user flow will be:
- Launch Application
- Generate User Unique Identifier
This Unique identifier is derived using only users’ mobile device attributes and does not use any personal information. The identifier generated is used on the backend to enable eSIM provisioning, data top-up and other such services. No user activity is logged in the process. - Generate User Master/ECDSA Keystore
- Fund User Master/ECDSA/Ethereum Wallet (not necessary for DevCon as we will having pre-purchased data bundles)
- Users proceeds to claim coupon code and install the eSIM
- Enjoy the data services!
Proposal
As the project progresses, we aim to use Devcon as an opportunity to release the product to the public and test it on a large scale. Since this is a non-profit product with the ambitious goal of onboarding the next billion users, we want to ensure a smooth UX and adhere to ecosystem principles.
Objective
Our goal is to test the application flow, provide a smooth UX within the telecom industry, and generate awareness among digital nomads. We hope to gather enough feedback to iterate and onboard the next wave of users.
How does that look like?
- PSE will sponsor this test for 2,000 attendees at a cost of $19,800.
- We welcome the Devcon team to sponsor more attendees.
- The fee covers costs payable to the telecom partner, such as Airalo or eSIM-GO.
- We will collaborate with organizers to distribute “claim codes.”
- Attendees will download our app via Google Play or the App Store.
- App will generate a device wallet in the background by using Device ID.
- Enter the “claim code” in the app.
- Install the eSIM data plan by following the instructions.
- Arrive in Thailand ready to enjoy free data for 10 days (50 GB).
- Submit feedback to the team.
Roadmap
Currently, the project is under development. We are integrating account abstraction into the smart contract.
Key milestones
- July to Mid-Aug: Flush out mobile app with front end and backend eng
- Mid-Aug: Submit the contract for audit by the PSE audit team.
- End-Aug: Conduct internal testing for QA.
- Sep: Scope out how to add zero-knowledge proofs to the OPEN Remote Sim Provisioning
- Mid-Sep: Complete the audit.
- End-Sep: Release the first wave of closed beta testing and bug fixing.
- Oct: Release the app.
- Mid-Oct: Open for the public to download and claim the free data plan.
Additional information
The blockchain-powered eSIM (app named Kokio), is a fully open-source project aimed at addressing long-standing issues in the telecom industry using cryptography and zero-knowledge proofs. The product requires partnership with telco aggregators such as Airalo for development.
For at least the next 12 months, the project will not generate any revenue and will only request users to cover costs payable to the aggregator. Although a KYC will be required, but we are using zero knowledge proof to verify the customer to ensure user’s privacy. The only data stored will be the user’s device ID and the output of KYC: nullifier.
Sign up for closed beta testing at: https://www.kokio.app/